Have you ever felt short of breath and wondered why? It’s an unsettling feeling when your body doesn’t seem to be getting enough oxygen, often leaving you gasping for air. While there can be many reasons for this sensation, one common cause is low blood oxygen, also known as hypoxemia. Let’s explore why this happens and what you can do about it.
Table of Contents
Understanding Blood Oxygen Levels
Blood oxygen levels suggest how much oxygen your red blood cells are carrying. Normally, these levels should be around 95-100%. Anything below this range can be alarming. But why is oxygen so critical? Oxygen fuels your cells, supporting everything from energy production to waste removal. When oxygen levels drop, your body might not function as efficiently.
How is Blood Oxygen Measured?
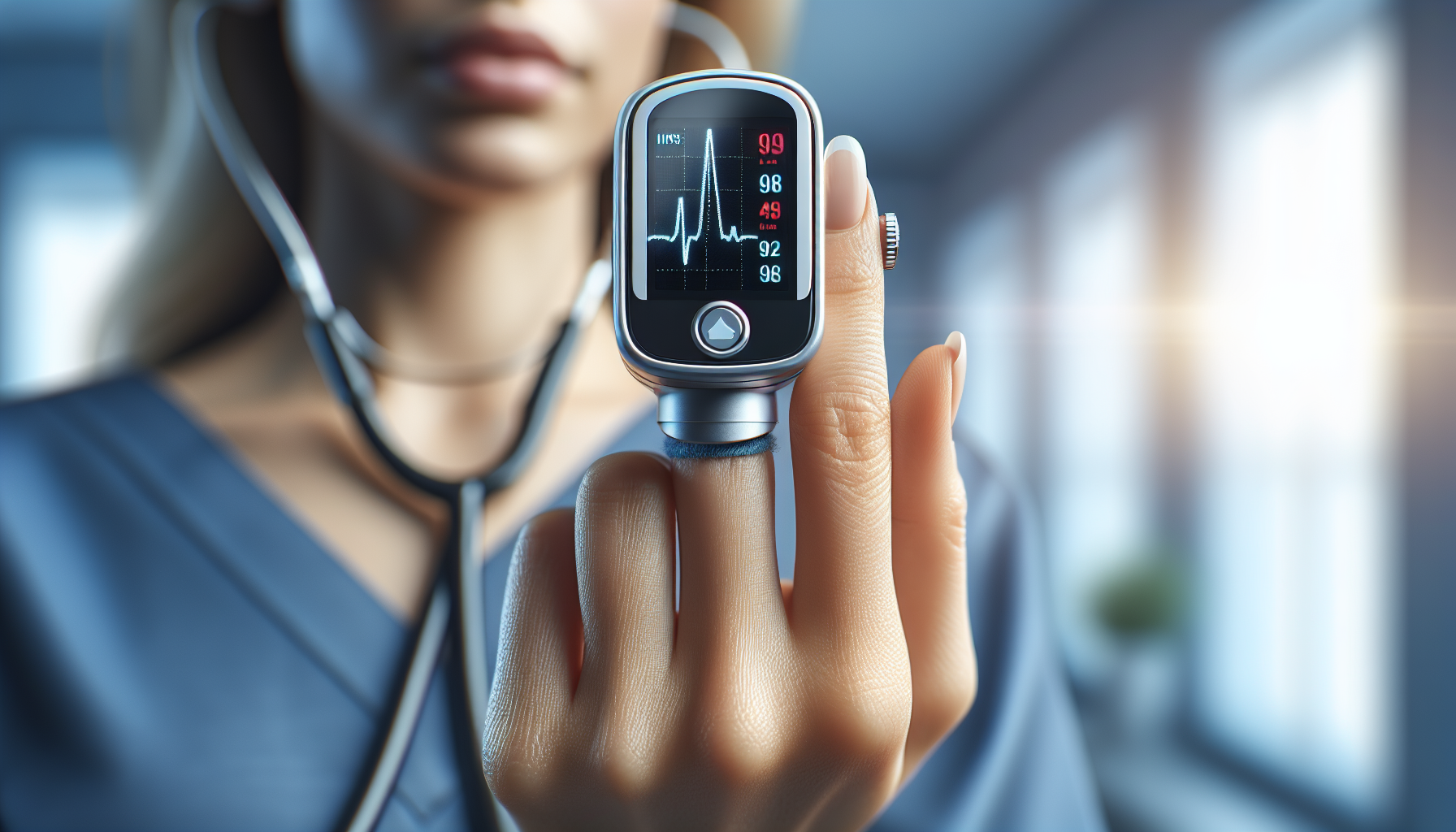
Blood oxygen levels are often measured using a device called a pulse oximeter. This small, clip-like device attaches to a body part, like your finger or earlobe. It measures how much light is absorbed by the blood, giving an estimation of the oxygen saturation. The result appears as a percentage, indicating how well your body is absorbing and using oxygen.
Causes of Low Blood Oxygen
Many factors can lead to low blood oxygen levels or hypoxemia. Identifying these causes helps in finding the right treatment. Let’s break down some of the most common causes.
Respiratory Conditions
Conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia can block oxygen from reaching your lungs. When your airways are inflamed or infected, it becomes difficult to breathe. This obstruction lowers the oxygen that can be absorbed into your blood.
Heart Problems
The heart pumps blood throughout your body, delivering oxygen to every cell. When it’s not pumping effectively due to heart failure or congenital heart defects, less oxygen-rich blood circulates. This can result in hypoxemia.
Anemia
Anemia is when you have fewer red blood cells than normal. Since these cells carry oxygen, a reduced number means less oxygen is transported. This can lead to symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath.
High Altitude
At higher altitudes, the air is thinner and contains less oxygen. If you’re not acclimated, everyone experiences lower blood oxygen levels to varying extents, with symptoms ranging from headaches to dizziness.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a condition where breathing stops momentarily during sleep. These interruptions can significantly decrease blood oxygen levels, affecting sleep quality and health.
Smoking
Smoking damages your lungs and decreases their efficiency in oxygen exchange. Smokers may naturally have lower blood oxygen levels due to substances like carbon monoxide binding to hemoglobin, reducing its oxygen-carrying capability.
Here’s a concise table highlighting these causes:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Respiratory Issues | Asthma, COPD, pneumonia affect airway and lungs. |
| Heart Problems | Heart inefficiencies reduce oxygen circulation. |
| Anemia | Fewer red blood cells mean less oxygen transport. |
| High Altitude | Thin air reduces oxygen availability. |
| Sleep Apnea | Breathing interruptions lower oxygen levels. |
| Smoking | Lung damage and reduced oxygen exchange. |
Symptoms of Low Blood Oxygen
Recognizing the signs of low blood oxygen is essential. While some symptoms might be obvious, others can be subtle. Here’s what to watch for.
Shortness of Breath
Feeling out of breath is the most common indicator. Even routine activities might leave you gasping.
Rapid Breathing
Your body may instinctively breathe faster to compensate for low oxygen, trying to draw in more air.
Elevated Heart Rate
A fast heartbeat can be your body’s way of circulating the available oxygen quickly to vital organs.
Fatigue and Weakness
Low oxygen levels can make you feel unusually tired or weak, affecting your daily activities.
Confusion and Dizziness
The brain can’t function properly without adequate oxygen, leading to confusion, dizziness, or even headaches.
Cyanosis
This is a bluish tint to the skin or lips, indicating severe hypoxemia. It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you notice this symptom.
Diagnosing Low Blood Oxygen
If you suspect low blood oxygen levels, it’s important to get a clinical diagnosis. This typically involves using a pulse oximeter or an arterial blood gas test to analyze the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
Pulse Oximetry
A non-invasive method that uses a sensor, typically attached to your fingertip, gives a quick assessment of your oxygen saturation.
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Test
This blood test measures the precise amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide, providing a detailed look at your blood gases.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies based on the underlying cause of low blood oxygen. Addressing the root problem is key to improving oxygen levels.
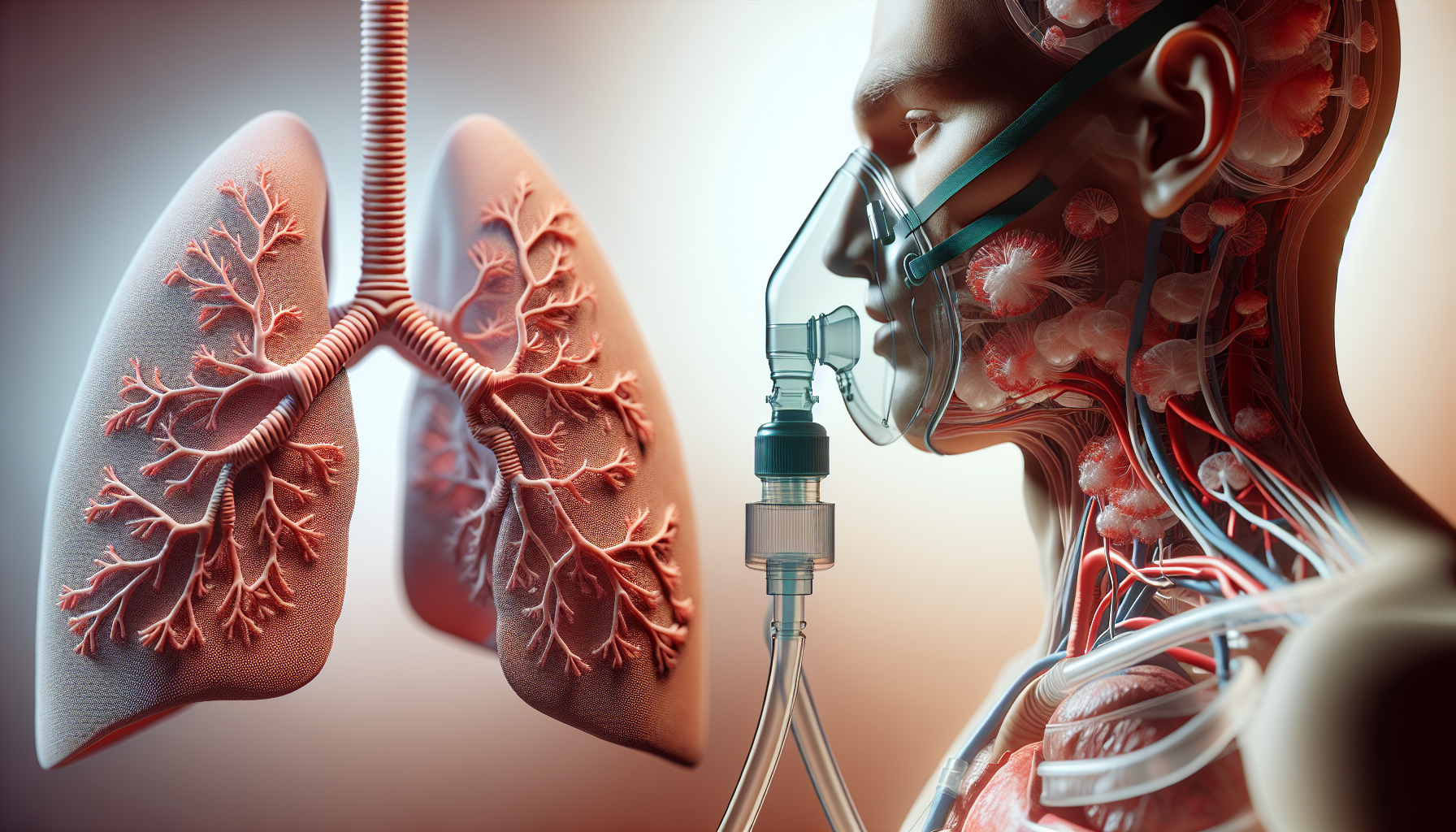
Oxygen Therapy
This involves supplementing oxygen to help improve oxygen levels in the blood. It’s provided via nasal prongs, a mask, or even a specialized hyperbaric chamber.
What is Hyperbaric Therapy?
Hyperbaric therapy, or Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), involves breathing 100% oxygen in a hyperbaric chamber where air pressure is higher than normal. This process increases the oxygen content in blood and tissues, aiding in healing and reducing inflammation. It’s beneficial for conditions like chronic wounds and decompression sickness.
Medications
For respiratory conditions, medications like bronchodilators or steroids may be prescribed to open up airways and reduce inflammation. Treating heart issues with medications like diuretics can also alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes
For long-term management, quitting smoking or relocating to lower altitudes might be recommended. Lifestyle modifications can be effective in preventing and managing symptoms of hypoxemia.
Prevention of Low Blood Oxygen
While not all cases can be prevented, there are ways to reduce risks associated with low blood oxygen.
Quit Smoking
Stopping smoking helps improve lung health, enhancing oxygen exchange and transportation in the body.
Manage Underlying Conditions
Keep chronic conditions like asthma or heart disease under control with regular medical check-ups and medications.
Stay Active
Engaging in regular physical activity can strengthen the cardiovascular system and improve overall oxygen circulation.
Monitor Your Health
Use devices like home pulse oximeters if you suffer from chronic respiratory conditions. This practice helps you keep track of your oxygen levels and seek professional help if they drop.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let’s address some common questions about low blood oxygen to provide further clarity.
What is considered a low oxygen level?
A blood oxygen level below 90% is typically seen as low, indicating hypoxemia. Levels under 80% can compromise organ function and may require immediate medical attention.
Why do I feel tired if my blood oxygen is low?
Your body relies on oxygen for energy. When levels drop, energy production in cells is affected, leading to fatigue.
How does hyperbaric therapy help with low blood oxygen?
Hyperbaric therapy increases the amount of oxygen your blood can carry, promoting healing, reducing inflammation, and supporting tissue repair.
Is dizziness a symptom of low blood oxygen?
Yes, dizziness can occur because the brain is highly sensitive to oxygen changes and requires a steady supply to function well.
Should I consult a doctor if I suspect low blood oxygen?
Yes. If you experience symptoms like dizziness, shortness of breath, or cyanosis, consult with a healthcare professional for evaluation.
Conclusion
Low blood oxygen is a condition that can affect your daily life and long-term health if left untreated. Understanding the causes—whether they’re due to underlying conditions like COPD, external factors like high altitude, or lifestyle choices like smoking—helps in effective management and treatment. Tools like pulse oximeters and therapies, including hyperbaric treatment, can play a critical role in managing oxygen levels. Should you experience any concerning symptoms consistently, contacting a professional such as Dr. Craig Henry or Dr. Aaron Hixon at Henry Chiropractic in Pensacola, FL, is a step toward taking control of your health. You’ve now got a comprehensive view of low blood oxygen. Keep an eye on those oxygen levels, and remember there are solutions to keep you breathing easy.
Contact Information:
Henry Chiropractic
1823 N 9th Ave
Pensacola, FL 32503
(850) 435-7777
Visit the Website