Have you ever felt out of breath after climbing a flight of stairs or noticed how athletes use oxygen tanks to recover faster during intense sports games? It leads one to wonder: at what point do you need supplemental oxygen? Understanding the ins and outs of supplemental oxygen can demystify this crucial aspect of healthcare. Perhaps you imagine complex machinery and medical scenarios, but in reality, it’s all about ensuring your body gets the oxygen it needs to function properly.
Table of Contents
Understanding Supplemental Oxygen
You might wonder why some people need supplemental oxygen. It’s simple—while breathing air, your lungs extract oxygen, which your bloodstream distributes to your tissues. Yet, certain conditions may hinder this process. When this happens, your body may require supplemental oxygen to perform essential functions more efficiently.
What is Supplemental Oxygen?
Supplemental oxygen refers to providing extra oxygen to those whose bodies can’t absorb enough from natural air. This might be needed temporarily or long-term, depending on the individual’s condition. Medical professionals typically prescribe oxygen therapy for individuals with lung diseases or other health issues hindering their lungs’ functionality.
Recognizing the Need for Supplemental Oxygen
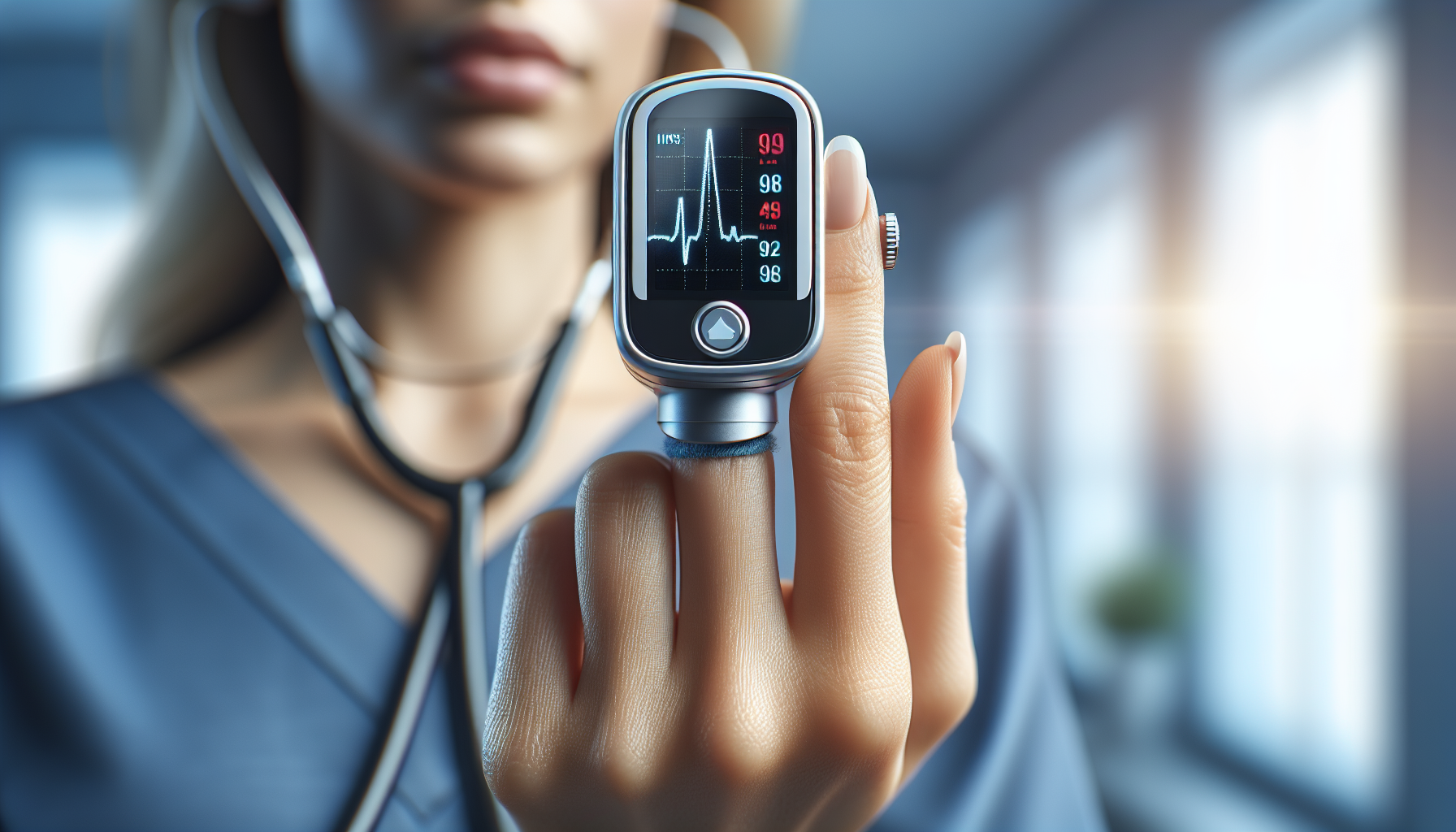
Determining the need for supplemental oxygen is vital. Oxygen levels are often assessed using a device called a pulse oximeter, which measures oxygen saturation (SpO2). Normal readings range from 95% to 100%. When levels drop below 90%, it suggests diminished oxygen in your blood, signaling the need for supplemental oxygen.
Supplemental oxygen becomes crucial under several conditions. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), sleep apnea, cystic fibrosis, heart failure, or pulmonary hypertension are examples. These medical conditions can restrict oxygen flow, making oxygen therapy necessary for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
The Science Behind Breathing and Oxygen Levels
To grasp why supplemental oxygen is essential, it’s helpful to understand how your body uses oxygen. Imagine your bloodstream like a delivery service, transporting oxygen to tissues that need it most. Your lungs act as a hub where this all begins.
How Lungs Process Oxygen
Your lungs are marvelous organs. With each breath, air fills your lungs, where oxygen passes into the bloodstream. This oxygen-rich blood then travels through your body, nourishing organs and tissues. Under normal conditions, this process runs smoothly, maintaining high oxygen saturation levels.
However, if impaired by illness or injury, your lungs might struggle to extract enough oxygen from each breath. As a result, fewer oxygen molecules are available to saturate your blood, affecting everything from brain function to physical stamina.
The Effect of Low Oxygen Levels
Low oxygen levels have immediate effects on your body. You may feel fatigued, dizzy, or short of breath. Long-term, untreated low oxygen levels could lead to organ damage, increased risk of infections, and significantly decreased quality of life. That’s why monitoring your oxygen levels and seeking appropriate medical advice is crucial when experiencing such symptoms.
Exploring Supplemental Oxygen Options
If your doctor recommends oxygen therapy, you might think about cumbersome devices. Rest assured, technological advances have made supplemental oxygen options far more convenient and accessible.
Types of Oxygen Therapy Devices
1. Oxygen Concentrators
Oxygen concentrators are common devices for long-term oxygen therapy. They filter room air, concentrate the oxygen, and deliver it through a nasal cannula or mask. Portable versions enable mobility, making them a popular choice for those who lead active lives.
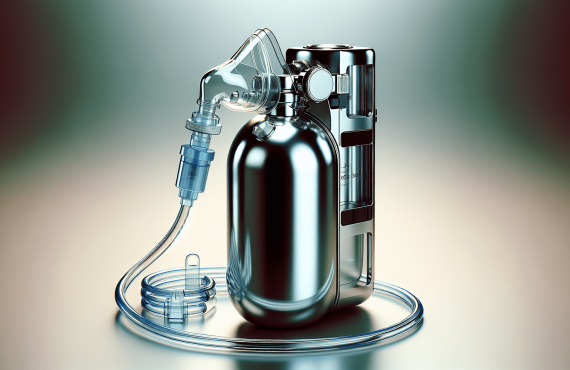
2. Compressed Gas Cylinders
These are perhaps the most recognizable form of supplemental oxygen. Oxygen gas is compressed into a cylinder and delivered through a mask or tube. Sizes range from large tanks for home use to small, portable ones for outings.
3. Liquid Oxygen Systems
Liquid oxygen systems convert oxygen into a liquid state, stored in compact containers. This allows for a higher oxygen volume in a smaller device. These systems are ideal for those needing a high, continuous flow of oxygen.
Benefits and Considerations
Each oxygen therapy type has its benefits and considerations. While oxygen concentrators are easy to use and need no refilling, compressed gas cylinders provide a higher flow for limited periods. Liquid oxygen systems offer portability but might require more frequent refills. Discussing your lifestyle and needs with your healthcare provider can help you choose the best option.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: A Special Mention
Turning our attention to a fascinating area of oxygen therapy: Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT). Though distinct from traditional supplemental oxygen, it holds significant value in specific medical contexts.
What is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy?
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy involves breathing 100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber. This treatment increases the oxygen concentration in your blood dramatically, promoting healing processes and tissue repair. It’s employed in situations like serious infections, wounds that won’t heal, or in some cases, carbon monoxide poisoning.
How Does It Work?
Under normal conditions, oxygen enters your blood primarily through red blood cells. In a hyperbaric chamber, the elevated pressure enables oxygen to dissolve in all body fluids, including plasma and lymph. This enhanced distribution accelerates healing by ensuring oxygen reaches all body areas, even those lacking in circulation.

Ask the Experts: Frequently Asked Questions about Supplemental Oxygen
Curiosity and concerns often arise when considering supplemental oxygen. Here we address some frequently asked questions to offer clarity.
FAQ 1: When should I seek medical advice about my oxygen levels?
If you consistently experience symptoms like difficulty breathing, persistent sleeping problems, or chronic fatigue, consulting a healthcare provider is wise. They can evaluate your oxygen levels and determine if oxygen therapy is right for you.
FAQ 2: Can I travel while on oxygen therapy?
Traveling with oxygen therapy is entirely possible. Planning is key. Portable oxygen concentrators have made traveling much more accessible. Always coordinate with your airline and healthcare provider before traveling to ensure you meet all safety requirements.
FAQ 3: Does using supplemental oxygen mean my condition is severe?
Not necessarily. Supplemental oxygen assists in maintaining optimal oxygen levels and can improve your quality of life, regardless of the severity of your condition. It’s a tool your healthcare provider uses to enhance your well-being.
FAQ 4: Are there side effects to using supplemental oxygen?
When used correctly, side effects are rare. However, excessive oxygen intake can cause dryness in the nasal passages or eyes. Your healthcare provider will guide you on proper usage to minimize risks.
FAQ 5: How frequently do I need to replace or refill my oxygen equipment?
The type of oxygen system determines how frequently you need to refill or replace equipment. Concentrators require minimal maintenance, whereas gas and liquid oxygen systems need refills. Regular check-ups ensure proper equipment function and oxygen delivery.
Living with Supplemental Oxygen: Tips for Success
Adjusting to life with supplemental oxygen can seem daunting initially, yet many find it significantly improves their quality of life.
Embrace the Learning Curve
Allow yourself time to adapt to the equipment and changes. Seek guidance from healthcare professionals, who can provide training on using the devices correctly and safely.
Incorporate Routine Monitoring
Regularly checking your oxygen levels with a pulse oximeter enables you and your healthcare provider to track your progress and adjust oxygen flow as needed.
Stay Active and Engaged
Don’t let supplementary oxygen deter you from activities you love. With portable options, many individuals lead thriving, active lifestyles. Whether it’s attending social events or engaging in light exercise, keeping active contributes positively to your mental and physical health.
Community and Support
Being part of a supportive community can significantly reduce the anxiety or uncertainty when using supplemental oxygen. Engage with groups or forums of others on similar journeys, where experiences and advice are shared openly.
Nearby Healthcare Support: Henry Chiropractic
If you reside in the Pensacola area, support and advice are close at hand. Dr. Craig Henry and Dr. Aaron Hixon at Henry Chiropractic offer expert guidance. Their personalized care approaches ensure you navigate your health journey feeling informed and supported.
Contact Information:
- Henry Chiropractic
- Address: 1823 N 9th Ave, Pensacola, FL 32503
- Phone: (850) 435-7777
- Website: drcraighenry.com
By staying informed and embracing expert advice, you can master managing supplemental oxygen. It’s a tool meant to enhance your daily life, ensuring you breathe easier every step of the way.