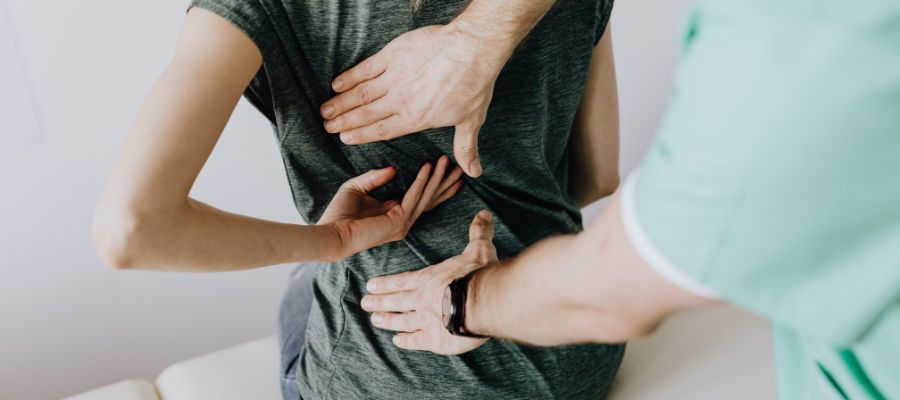
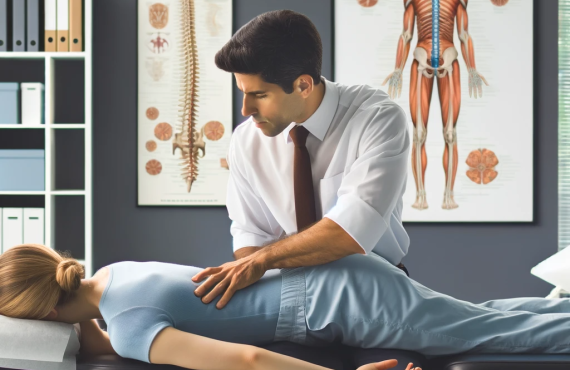
Are you tired of living with constant back pain? Look no further than the “back pain treatment” offered by Henry Chiropractic in Pensacola, FL. This revolutionary treatment is designed to provide you with the relief you’ve been longing for. Whether you’re struggling with acute or chronic back pain, Henry Chiropractic has the expertise and resources to address your specific needs. Say goodbye to discomfort and start living a pain-free life with the help of their top-notch back pain treatment.
Table of Contents
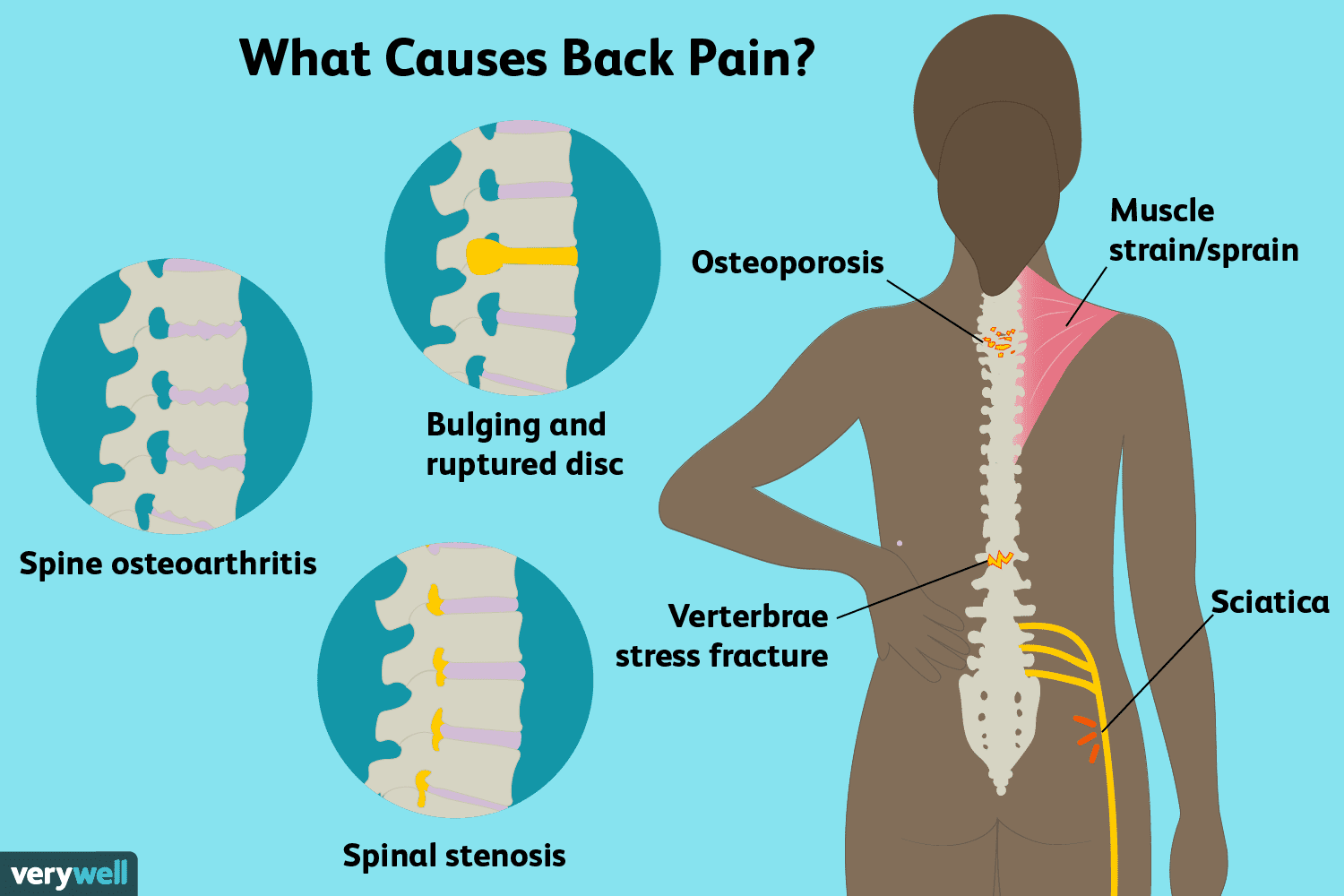
Causes of Back Pain
Muscle Strain
Muscle strain is one of the most common causes of back pain. This occurs when the muscles in the back are stretched or torn due to overuse or improper lifting techniques. It can be caused by activities such as heavy lifting, sudden movements, or poor posture. Muscle strain can lead to inflammation and pain in the affected area.
Ligament Sprain
A ligament sprain occurs when the ligaments in the back are stretched or torn. This can be caused by sudden movements, trauma, or repetitive stress. Ligament sprains can result in pain, swelling, and difficulty in movement. It is important to rest and avoid further stress to allow the ligaments to heal properly.
Herniated Disc
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner portion of a disc in the spine pushes through the outer layer. This can put pressure on nearby nerves, causing pain and discomfort. Herniated discs can be caused by age-related wear and tear, injury, or excessive strain on the spine. Treatment may include rest, medication, physical therapy, or in severe cases, surgery.
Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease is a condition where the discs in the spine start to break down and lose their cushioning ability. It is commonly caused by the natural aging process, but can also be accelerated by factors such as obesity, smoking, and physical stress. Degenerative disc disease can lead to chronic back pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal, which puts pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This can cause back pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected area. Spinal stenosis is commonly caused by age-related degeneration of the spine, but can also be a result of conditions such as arthritis or spinal tumors.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal curvature of the spine. This can cause back pain, muscle stiffness, and uneven shoulders or hips. Scoliosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, muscle imbalances, or underlying medical conditions. Treatment options may include physical therapy, bracing, or in severe cases, surgery.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by the loss of bone density, making the bones more prone to fractures and injuries. This can lead to back pain and an increased risk of vertebral compression fractures. Osteoporosis is commonly caused by hormonal changes, aging, or certain medications. Treatment may include medication, exercise, and lifestyle modifications.
Arthritis
Arthritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the joints, including those in the spine. This can cause back pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. The most common types of arthritis affecting the spine are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment options may include medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Spinal Tumor
A spinal tumor is an abnormal growth of cells within the spinal cord or the surrounding structures. This can cause back pain, neurological symptoms, and mobility issues. Spinal tumors can be benign or malignant and may require a combination of treatments, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
Infection
Infection in the spine, also known as spinal infection or vertebral osteomyelitis, can cause inflammation and pain in the back. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and may result from an infection in another part of the body spreading to the spine. Treatment usually involves antibiotics or antifungal medications, as well as drainage of any abscesses.
Symptoms of Back Pain
Localized Pain
Localized pain is a common symptom of back pain. It refers to pain that is confined to a specific area of the back. The pain can vary in intensity and may worsen with movement or certain activities.
Radiating Pain
Radiating pain is a symptom that occurs when the pain in the back spreads to other areas of the body, such as the buttocks, legs, or arms. This is often caused by compression or irritation of nerves in the spine.
Muscle Stiffness
Muscle stiffness can accompany back pain and can make it difficult to move or perform everyday activities. It is often caused by muscle imbalances, tension, or inflammation.
Limited Range of Motion
Limited range of motion refers to a decreased ability to move the back freely and comfortably. This can be caused by pain, muscle stiffness, or joint dysfunction.
Muscle Spasms
Muscle spasms are involuntary contractions of the muscles in the back. They can be painful and can cause the back to feel tense and rigid. Muscle spasms are often a result of overuse, muscle strain, or underlying conditions.
Pain with Movement
Pain that worsens with movement is a common symptom of back pain. Certain activities or positions may exacerbate the pain, making it difficult to perform daily tasks or engage in physical activities.
Pain that Worsens with Time
Back pain that worsens over time can indicate a progressive condition or an underlying structural problem. It is important to seek medical attention if the pain becomes more severe or persistent.
Numbness or Tingling
Numbness or tingling sensations in the back, buttocks, legs, or arms can be a sign of nerve compression or irritation. This can occur due to herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or other conditions affecting the nerves in the spine.
Weakness
Weakness in the back or the extremities can occur as a result of nerve compression or muscle imbalances. It can make it difficult to perform daily activities or maintain proper posture.
Loss of Bladder or Bowel Control
Loss of bladder or bowel control is a serious symptom that requires immediate medical attention. It can indicate a severe compression of the spinal cord or cauda equina syndrome, which requires prompt treatment to avoid permanent damage.
Diagnosis of Back Pain
Medical History
A thorough medical history is important in diagnosing the cause of back pain. The healthcare provider will ask about the onset and duration of the pain, any previous injuries, underlying health conditions, and any factors that worsen or alleviate the pain.
Physical Examination
A physical examination can help assess the range of motion, strength, and flexibility of the back. The healthcare provider may also perform specific tests to evaluate the function of the nerves and assess for any structural abnormalities.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans, may be ordered to visualize the bones, discs, and soft tissues of the spine. These can provide valuable information about the underlying cause of back pain, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or fractures.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests, such as blood tests, may be ordered to rule out any underlying inflammatory or infectious causes of back pain. These tests can help detect conditions such as arthritis or infections in the spine.
Nerve Studies
Nerve studies, such as electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies, can help evaluate the function of the nerves in the back. These tests can assess for any nerve damage or compression and can provide valuable information about the severity and location of the problem.
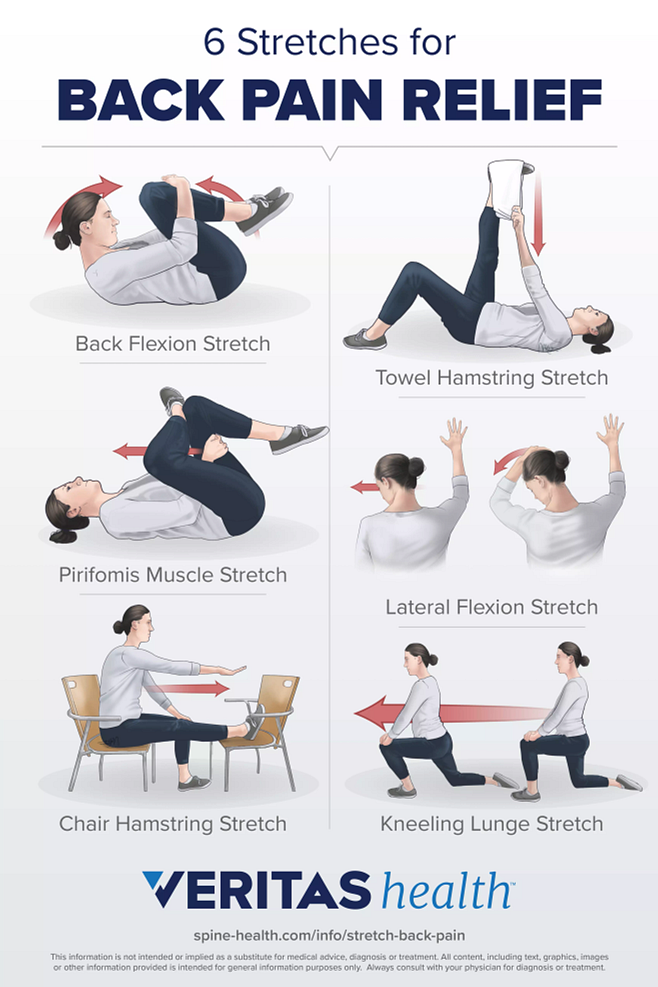
Conservative Treatments for Back Pain
Rest
Resting the back can help alleviate pain and promote healing. It is important to avoid any activities that worsen the pain and to provide adequate support to the back while resting.
Ice and Heat Therapy
Applying ice or heat to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Ice packs or cold compresses can be used in the acute phase of back pain, while heat therapy, such as hot packs or warm showers, can help relax tight muscles and improve blood circulation.
Pain Medication
Over-the-counter pain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen, can be used to manage mild to moderate back pain. Prescription medications may be recommended for more severe pain or when conservative treatments are not effective.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help improve the strength, flexibility, and stability of the back. It may involve a combination of exercises, stretches, manual therapy techniques, and modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal disorders, including back pain. Chiropractors use manual adjustments and other therapies to restore proper alignment and function of the spine.
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy can help relax tight muscles, improve circulation, and reduce pain and inflammation in the back. Different techniques, such as Swedish massage, deep tissue massage, or trigger point therapy, may be used depending on the individual’s specific needs.
Acupuncture
acupuncture is a traditional Chinese therapy that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. It is believed to help balance the body’s energy and promote healing. Acupuncture may be used as an alternative treatment for back pain.
Exercise and Stretching
Regular exercise and stretching can help improve the strength and flexibility of the back muscles, reducing the risk of pain and injury. Low-impact activities, such as swimming or walking, are often recommended for individuals with back pain.
Posture Improvement
Maintaining good posture can help alleviate back pain and prevent further problems. This involves sitting and standing with proper spinal alignment, using ergonomic furniture, and being mindful of body mechanics during activities.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on the back and decrease the risk of developing back pain. Weight loss through a combination of a healthy diet and regular exercise can help improve overall spinal health.
Alternative Therapies for Back Pain
Mindfulness Meditation
Mindfulness meditation involves focusing on the present moment and cultivating a non-judgmental awareness. It may help reduce stress, improve mood, and alleviate back pain by promoting relaxation and reducing muscle tension.

Yoga
Yoga combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to improve flexibility, strength, and overall well-being. It can help alleviate back pain by stretching and strengthening the muscles, as well as promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
Tai Chi
Tai Chi is a low-impact exercise that involves slow, graceful movements and deep breathing. It can help improve balance, flexibility, and strength, and may provide relief from back pain by promoting relaxation and improving posture.
Pilates
Pilates is a form of exercise that focuses on core strength, flexibility, and body awareness. It involves precise movements and controlled breathing, which can help improve posture, stabilize the spine, and reduce back pain.
Biofeedback
Biofeedback is a technique that uses electronic devices to provide information about the body’s physiological responses. It can help individuals gain control over physical processes, such as muscle tension, and may be beneficial in managing back pain.
Herbal Remedies
Certain herbs and supplements, such as turmeric, devil’s claw, or ginger, have been traditionally used to manage pain and inflammation. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using any herbal remedies, as they can interact with medications or have side effects.
Topical Creams and Gels
Topical creams and gels containing ingredients such as menthol, capsaicin, or lidocaine can provide temporary relief from back pain. These products work by numbing the area, reducing inflammation, or blocking pain signals.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
TENS is a therapy that uses low-voltage electrical currents to provide pain relief. It works by stimulating the nerves and interfering with pain signals. TENS devices are portable and can be used at home under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Ultrasound Therapy
Ultrasound therapy uses high-frequency sound waves to provide deep heat to the tissues. It can help reduce pain, inflammation, and muscle spasms in the back. Ultrasound therapy is often performed by a healthcare professional.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a type of therapy that focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It can help individuals with chronic back pain manage their symptoms by promoting positive coping strategies and reducing pain-related distress.
Interventional Procedures for Back Pain
Epidural Steroid Injections
Epidural steroid injections involve the injection of a corticosteroid medication into the epidural space around the spinal cord. This can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain in the back. Epidural steroid injections are typically performed by a healthcare professional.
Facet Joint Injections
Facet joint injections target the small joints in the spine called facet joints. A combination of local anesthetic and a corticosteroid medication is injected into the affected joints to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
Nerve Block Injections
Nerve block injections involve the injection of a local anesthetic or a combination of local anesthetic and steroid medication to block the pain signals from specific nerves in the back. This can provide temporary or long-lasting relief from back pain.
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is a procedure that uses heat generated by radiofrequency waves to disrupt the nerve signals responsible for transmitting pain. It can provide long-lasting pain relief by temporarily or permanently preventing the affected nerves from sending pain signals.
Spinal Cord Stimulation
Spinal cord stimulation involves the implantation of a device that delivers mild electrical impulses to the spinal cord. These impulses interfere with the pain signals, providing pain relief. Spinal cord stimulation is typically used for individuals with chronic, severe back pain who have not responded to other treatments.
Intradiscal Electrothermal Therapy (IDET)
Intradiscal electrothermal therapy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the insertion of a heating wire into the affected disc. The wire is heated to a specific temperature, which cauterizes the disc and ablates the nerve fibers responsible for transmitting pain.
Percutaneous Discectomy
Percutaneous discectomy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the removal of a herniated disc using a specialized tool inserted through a small incision. This can relieve pressure on the affected nerves and alleviate back pain.
Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty
Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are minimally invasive procedures used to treat vertebral compression fractures. These procedures involve the injection of bone cement into the fractured vertebra, stabilizing the bone and reducing pain.
Trigger Point Injections
Trigger point injections involve the injection of a local anesthetic or a corticosteroid medication into tender, knotted muscles in the back known as trigger points. This can help relax the muscles and alleviate pain.
Sacroiliac Joint Injections
Sacroiliac joint injections involve the injection of a local anesthetic or a combination of local anesthetic and steroid medication into the sacroiliac joint, located at the base of the spine. This can provide pain relief for individuals with sacroiliac joint dysfunction or inflammation.
Surgical Options for Back Pain
Discectomy
Discectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of a portion or the entire herniated disc that is causing pressure on the nerves in the back. This can alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Laminectomy
Laminectomy, also known as decompression surgery, involves the removal of the lamina, a portion of the vertebral bone, to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. This can be performed to treat conditions such as spinal stenosis or herniated discs.
Spinal Fusion
Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure that involves joining two or more vertebrae together using bone grafts or metal hardware. This can stabilize the spine and reduce pain caused by conditions such as degenerative disc disease or spinal instability.
Artificial Disc Replacement
Artificial disc replacement is a surgical procedure that involves removing a damaged or degenerated disc and replacing it with an artificial disc. This can preserve motion in the spine and alleviate pain.
Foraminotomy
Foraminotomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing a portion of the bone or tissue that is causing compression of the nerve roots as they exit the spinal column. This can relieve pain and improve nerve function.

Microdiscectomy
Microdiscectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves the removal of a herniated disc using a specialized microscope and surgical instruments. This can relieve pressure on the affected nerves and alleviate pain.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
Minimally invasive spine surgery is a technique that uses small incisions and specialized surgical instruments to treat various spinal conditions. This approach can result in less tissue damage, reduced scarring, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty
Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty, mentioned earlier as interventional procedures, can also be considered surgical options for individuals with vertebral compression fractures. These procedures involve the injection of bone cement into the fractured vertebra to stabilize the bone and reduce pain.
Coccygectomy
Coccygectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the coccyx, or tailbone. This procedure may be considered in rare cases of severe, chronic coccydynia (tailbone pain) that does not respond to conservative treatments.
Spinal Decompression
Spinal decompression is a surgical procedure that involves removing a portion of the bone or tissue that is causing compression of the spinal cord or nerves. This can relieve pain and improve nerve function in conditions such as spinal stenosis or herniated discs.
Preventing Back Pain
Exercise Regularly
Regular exercise, including activities that strengthen the core and back muscles, can help prevent back pain. It can also improve flexibility and promote overall spinal health.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on the back and decrease the risk of developing back pain. A combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise is key to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Practice Good Posture
Maintaining good posture can help prevent back pain. This involves sitting and standing with proper spinal alignment, using ergonomic furniture, and being mindful of body mechanics during activities.
Use Proper Lifting Techniques
Using proper lifting techniques can help prevent back injuries. When lifting heavy objects, it is important to bend at the knees, keep the back straight, and use the leg muscles to lift.
Take Frequent Breaks from Sitting
Sitting for prolonged periods can put stress on the back and contribute to back pain. Taking frequent breaks to stand up, stretch, and walk around can help alleviate this stress and promote spinal health.
Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing
Both prolonged sitting and standing can strain the back and contribute to back pain. It is important to alternate between sitting and standing, and to use supportive chairs and footwear when necessary.
Support your Back during Sleep
Using a supportive mattress and pillow that is appropriate for your sleeping position can help maintain the natural alignment of the spine and prevent back pain. Sleeping on the side with a pillow between the knees can also help maintain proper spinal alignment.
Wear Comfortable Shoes
Wearing comfortable, supportive shoes can help maintain proper alignment of the spine and reduce the risk of developing back pain. It is important to choose shoes that provide adequate cushioning and arch support.
Quit Smoking
Smoking can contribute to various health problems, including back pain. Smoking decreases blood flow to the spinal discs, which can contribute to degeneration and increased risk of back pain. Quitting smoking can improve overall spinal health.
Manage Stress
Stress can contribute to muscle tension and increased perception of pain. Practicing stress-management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation or engaging in relaxing activities, can help reduce stress and alleviate back pain.
Seeking Professional Help for Back Pain
When to See a Doctor
It is important to seek medical attention if back pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms such as numbness, weakness, or loss of bladder or bowel control. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires prompt treatment.
Choosing the Right Provider
When seeking professional help for back pain, it is important to choose the right healthcare provider. Depending on the severity and cause of the back pain, options may include primary care physicians, orthopedic specialists, neurologists, or chiropractors.
Importance of Personalized Care
Each individual and case of back pain is unique, and a personalized approach to treatment is essential for achieving the best outcomes. This involves a thorough evaluation of the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and goals, as well as considering any underlying conditions or risk factors.
Finding the Best Back Pain Specialist
Finding the best back pain specialist involves considering factors such as experience, expertise, and patient reviews. It is important to choose a healthcare provider who understands your specific needs and has a track record of successfully treating back pain.
Testimonials from Henry Chiropractic Patients
Henry Chiropractic in Pensacola, FL is known for its exceptional patient care and positive outcomes in treating back pain. Numerous patients have provided testimonials praising the expertise, compassion, and effective treatment they received at Henry Chiropractic.
Why Choose Henry Chiropractic for Back Pain Treatment
Henry Chiropractic is a trusted provider of back pain treatment, offering a comprehensive approach that includes personalized care, advanced techniques, and a focus on promoting overall spinal health. The team at Henry Chiropractic is dedicated to helping patients achieve long-term relief from back pain and improving their quality of life.
Henry Chiropractic’s Approach to Back Pain
At Henry Chiropractic, the approach to back pain treatment involves a combination of conservative therapies, alternative treatments, and a patient-centered approach. The team of experienced chiropractors and healthcare professionals at Henry Chiropractic work closely with each patient to develop a customized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.
Conclusion
Back pain is a common condition that can have various causes and a wide range of symptoms. It can significantly impact an individual’s daily life, making it important to seek effective treatment. With the help of healthcare professionals and a commitment to preventive measures, individuals can find relief from back pain and improve their overall spinal health. For the best back pain treatment, consider visiting Henry Chiropractic in Pensacola, FL. Their team of experts is dedicated to providing personalized care and effective solutions for back pain.