Have you ever wondered about when a simple breath might need a little extra support? From marathon runners to mountaineers, oxygen plays varied roles in our lives. But, at times, it’s a vital lifeline in medical settings. Let’s consider the scenarios where patients truly benefit from oxygen therapy.
Table of Contents
What is Oxygen Therapy?
Oxygen therapy involves supplementing the oxygen that you naturally breathe. For individuals with conditions that impair their ability to absorb sufficient oxygen through normal breathing, this can be a game changer. While it might sound complex, at its core, it’s about ensuring your body gets the oxygen it so desperately needs–even when it struggles on its own.
How Does It Work?
Under normal circumstances, your lungs process the oxygen from the atmosphere and deliver it to tissues via the bloodstream. With oxygen therapy, an increased concentration is supplied, often through devices like nasal cannulas or masks. For some, this can be lifesaving, as it supports body functions that otherwise falter due to low oxygen levels.
Why Oxygen is Essential?
Every cell in your body relies on oxygen to function optimally. From brain activity to muscle function, oxygen is critical. When your levels dip, a range of symptoms can occur, from shortness of breath to cognitive issues–sometimes it’s severe enough to threaten life. Oxygen therapy maintains optimal performance of your body’s vital systems, especially the heart and brain.
Who Would Benefit from Oxygen Therapy?
Different patients require oxygen for varied reasons. Understanding these conditions helps in recognizing why oxygen therapy is so widely used in medical treatments.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD encompasses diseases like emphysema and chronic bronchitis, which obstruct airflow to the lungs. If you have COPD, your body struggles to get enough oxygen, making breathing laborious. Oxygen therapy can ease your breathing difficulties by providing consistent oxygen levels, allowing you to maintain a more active lifestyle.
Pneumonia
If you’ve ever battled pneumonia, you know how it can impair your lung function drastically. With this infection, oxygen therapy often aids recovery, ensuring you receive the needed oxygen despite inflamed and fluid-filled air sacs.
Heart Failure
Heart failure affects oxygen delivery because your heart can’t pump efficiently. Oxygen therapy ensures that, even with a weakened heart, your body tissues receive much-needed oxygen, supporting better health outcomes.
Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea causes a sudden drop in blood oxygen during sleep. In severe cases, oxygen therapy can be combined with CPAP machines to ensure stable oxygen levels throughout the night, improving sleep quality and overall health.
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic Fibrosis leads to the buildup of thick mucus in the lungs, disrupting oxygen transport. For these patients, oxygen therapy assists in delivering oxygen even when natural lung function is compromised.
Asthma
During severe asthma attacks, airways constrict, reducing oxygen flow. In acute cases, oxygen therapy can stabilize oxygen levels, offering quick relief and reducing potential complications.

Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy is a specialized form implemented for specific conditions. By breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, patients can experience profound health benefits.
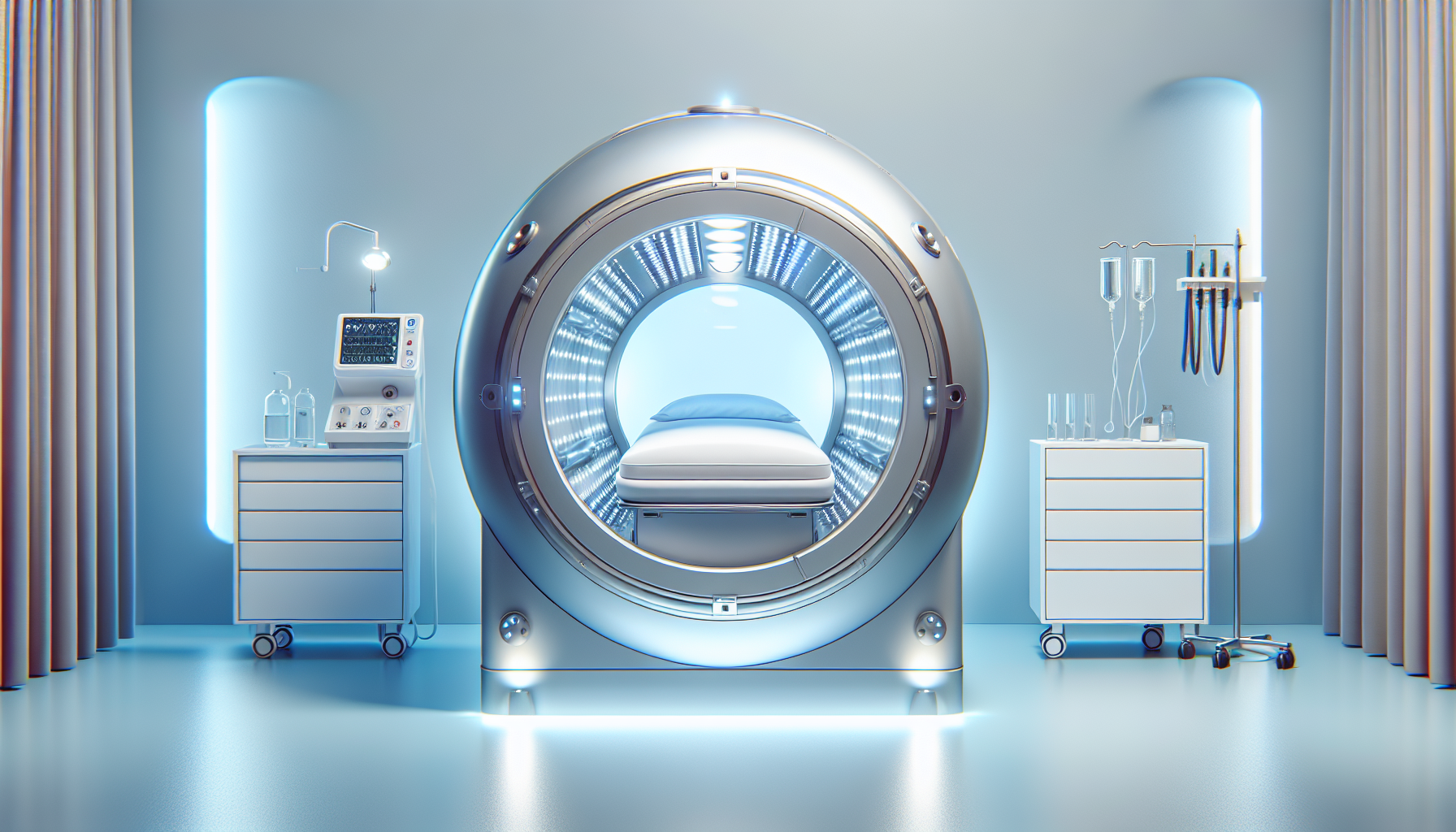
What Is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy?
HBOT involves inhaling 100% oxygen at higher pressures than normal atmospheric conditions. It’s typically used in a chamber where the environment is carefully controlled to boost the effectiveness of oxygen intake.
How Does HBOT Work?
When under increased pressure, oxygen is dissolved directly into your plasma, allowing it to reach tissues and areas that might have a blocked or limited supply. This can accelerate healing processes, reduce inflammation, and improve immune responses.
Benefits of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
-
Enhanced Wound Healing: HBOT promotes angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, crucial for healing stubborn or severe wounds.
-
Infection Control: High oxygen levels can restrict certain bacterial growth, supporting infection control.
-
Reduced Edema: It helps lower inflammation and swelling, hastening recovery.
FAQ
What are the Risks of Oxygen Therapy?
Though beneficial, oxygen therapy has potential risks. Overuse can cause oxygen toxicity leading to lung damage. A healthcare provider helps determine precise usage to avoid complications.
Can Oxygen Therapy Be Used at Home?
Yes, many patients continue therapy at home with portable oxygen systems. Compliance and regular monitoring are essential for effective home use.
Is Oxygen Therapy Addictive?
Oxygen therapy addresses physical needs and is not addictive. Dependency may arise from the underlying condition, not the therapy itself.
Does Oxygen Therapy Enhance Athletic Performance?
While oxygen can improve recovery in certain cases, using it for performance enhancement without medical supervision is not recommended.
How Do I Know If I Need Oxygen Therapy?
Symptoms like chronic shortness of breath, confusion, or low oxygen readings from pulse oximeters could indicate a need. Consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.

Discover Skills at Henry Chiropractic
While oxygen plays a crucial role in certain medical conditions, overall health also relies on other supports such as chiropractic care. At Henry Chiropractic, Dr. Craig Henry and Dr. Aaron Hixon offer comprehensive services in Pensacola, Florida, emphasizing natural health improvements. Whether tackling pain, enhancing mobility, or striving for general wellness, their expert care supports various health needs.
For any chiropractic needs, contact:
Henry Chiropractic
1823 N 9th Ave
Pensacola, FL 32503
(850) 435-7777
drcraighenry.com
In essence, oxygen therapy provides critical support in a myriad of health challenges. Being informed helps you understand when oxygen could be a treatment for you or a loved one. Remember, it’s about breathing easy and ensuring your body receives the resources it needs to thrive.